Indoor Tanning
The tan fades but the damage lasts forever.
Indoor tanning is dangerous. It exposes you to high levels of ultraviolet radiation in a short time. Tanning beds are much more intense than natural sun exposure.
Health concerns:
- Exposure to ultraviolet radiation increases the risk of skin cancers, including melanoma.
- Melanoma is the most deadly form of skin cancer.
- Exposure to ultraviolet radiation also can cause cataracts, blinding eye diseases, and cancers of the eye.
- Tanning weakens your immune system and can worsen some medical conditions.

Indoor tanning is particularly dangerous for younger users. The more you tan, the greater your risk for skin cancer.
- If you indoor tan before age 30, you have a 75 percent increased risk of melanoma.
- Even one tanning session increases the risk of melanoma. Your risk increases every time you tan.
- The incidence of melanoma has dramatically increased among young women. Melanoma is the third most common cancer in people from 15 to 39.
Indoor tanning is horrible for your skin.
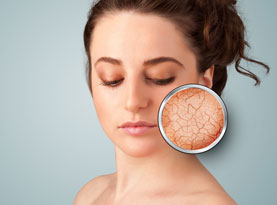
- It changes skin texture.
- It causes your skin to age earlier with sagging, wrinkles, and age spots.
- Tanning while using some medications or cosmetics can increase sensitivity to ultraviolet radiation and cause burns, itching, scaling, rashes or swelling.
There is no such thing as a safe tan.
- A tan is what happens when your skin is damaged from ultraviolet rays.
- A base tan is not a safe tan. It does not protect you from further burning or sun damage.
- Indoor tanning is not a safe way to get vitamin D.
- You can get more than a tan from a tanning bed! If the tanning bed isn't clean, you could get genital warts, skin rashes, skin warts, flaky discolored patches on your skin, and more.
Under the law, no one under 18 years old can use an indoor tanning bed, booth or sunlamp.
- People who are 18 or older must show a driver's license or photo identification.
- Parents can make a difference: say no to tanning for yourself and your kids.